Drlogy
Healthcare organization
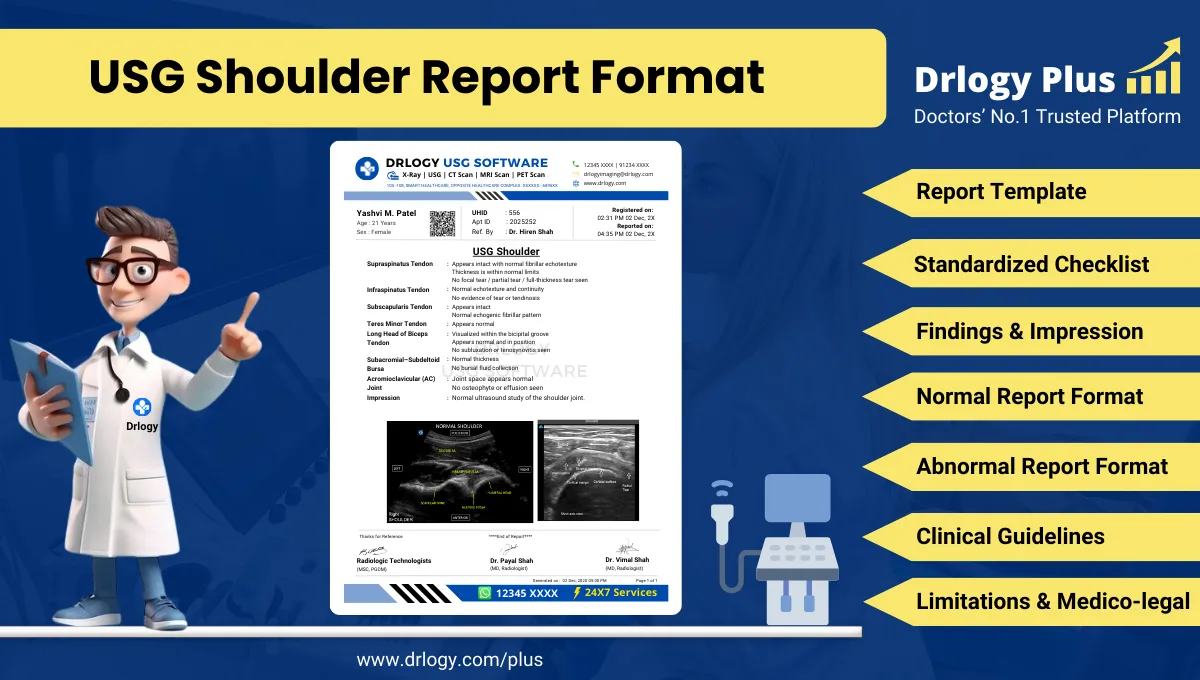
Pelvis Ultrasound Report Format for Radiologists
What Is a Pelvis Ultrasound Report Format?
A Pelvis ultrasound report format is a standardized professional structure for documenting ultrasonographic evaluation of pelvic organs using consistent anatomical terminology and measurement conventions.
It functions as a clinical communication tool supporting diagnosis, referrals, follow-up decisions, and longitudinal comparison across serial pelvic imaging examinations.
It is a medico-legal record defining examination scope, technique adequacy, objective findings, conservative interpretation, and documented limitations in alignment with accepted radiology standards.
Check:
Best AI-Based Ultrasound Reporting Software for Radiologists
Clinical Importance of a Standardized Pelvis Ultrasound Report Format
- Diagnostic clarity by ensuring systematic documentation of pelvic organs, their size, morphology, echotexture, and spatial relationships.
- Inter-doctor communication through consistent terminology understood across gynecology, urology, surgery, oncology, and primary care.
- Reporting consistency by reducing inter-radiologist variability in describing uterine, ovarian, prostatic, and bladder findings.
- Patient safety by minimizing omission of clinically critical findings such as adnexal masses, free fluid, or urinary retention.
- Medico-legal protection by documenting technique, limitations, and conservative impressions appropriate to ultrasound capabilities.
A standardized pelvis ultrasound report format improves reliability, comparability, and audit readiness across routine and high-volume diagnostic settings.
Why Manual Reporting Often Fails to Maintain Standardization at Scale
- Inter-radiologist variability in pelvic organ descriptors, measurements, and impression phrasing leads to inconsistent clinical interpretation.
- Missed sections in high-volume settings commonly include adnexal assessment, post-void bladder evaluation, or pelvic free fluid documentation.
- Terminology inconsistency such as bulky uterus versus enlarged uterus or cystic adnexal lesion versus ovarian cyst complicates follow-up.
- Audit challenges arise because narrative free-text reports lack structured fields required for quality assurance and medico-legal review.
Software-assisted structured reporting improves completeness and uniformity while preserving professional judgment.
Indications for Pelvis Ultrasound
- Lower abdominal or pelvic pain evaluation
- Abnormal uterine bleeding assessment
- Evaluation of pelvic masses detected clinically
- Infertility assessment and follicular monitoring
- Suspected ovarian or adnexal pathology
- Follow-up of known pelvic lesions
- Urinary symptoms with suspected bladder or prostate involvement
- Postoperative or post-intervention pelvic assessment
A concise and focused indication ensures clinically relevant reporting and a targeted impression.
Pre-Examination Details to Be Documented
- Patiententifiers including name, age, sex, unique, accession number, study date and time.
- Referral details including referring clinician, department, and clinical indication.
- Clinical notes such as menstrual history, pregnancy status, urinary symptoms, infertility context, or prior pelvic imaging.
- Preparation status including bladder filling adequacy and fasting status if relevant.
- Safety checks including correct patient verification, pregnancy status confirmation when applicable, and correct study labeling.
How Reporting Software Ensures Complete Pre-Examination Documentation
- Mandatory field enforcement ensures patiententity, indication, and preparation status are completed before report finalization.
- Safety checklist compliance standardizes pregnancy status confirmation and correct study verification.
- Clinical note traceability links referral context and prior imaging informationectly to the report.
- Implementation example: Drlogy Radiology Reporting Software supports structured pelvis ultrasound templates with compulsory pre-examination documentation fields.
Standard Sections of a Pelvis Ultrasound Report Format
- Patient & Study Information
- Clinical History / Indication
- Technique / Protocol
- Findings (organ/system-wise pelvic evaluation)
- Impression / Conclusion
- Limitations of the Study
- Recommendations & Follow-Up (if applicable)
A consistent section order enhances readability, completeness, and medico-legal defensibility.
Patient & Study Information Section
This section establishes traceability and accountability:
- Patient demographics and uniqueentifiers
- Study date, time, and accession number
- Referring clinician and department
- Examination name and scope (transabdominal, transvaginal, transrectal where applicable)
- Prior imaging references if available
Clinical History / Indication Section
Best practices include:
- Clear documentation of presenting symptoms or clinical question
- Relevant gynecological, urological, or surgical history
- Menstrual and obstetric history when applicable
- Avoidance of speculative or unrelated information
Technique / Protocol Section
- Positioning: supine with appropriate pelvic exposure.
- Approach: transabdominal ultrasound with full bladder; transvaginal or transrectal approach when indicated and consented.
- Views: longitudinal and transverse pelvic organ views.
- Transducer: curvilinear probe for transabdominal; high-frequency endocavitary probe for transvaginal/transrectal imaging.
- Doppler usage: documented when vascular assessment of pelvic organs or masses is performed.
Technique documentation defines examination scope and supports interpretive accuracy.
Findings Section – Organ/System-Wise Reporting
Pelvic findings should be documented objectively and systematically.
Uterus
- Size, position, and orientation
- Myometrial echotexture
- Endometrial thickness and appearance
- Presence of focal lesions such as fibroids
Ovaries / Adnexa
- Size and morphology of each ovary
- Follicular pattern
- Presence and characterization of cysts or masses
- Doppler vascularity when assessed
Pelvic Cavity
- Presence or absence of free fluid
- Location and amount if present
Urinary Bladder
- Wall thickness and contour
- Intraluminal contents
- Post-void residual volume if assessed
Objective description must precede interpretation, with explicit documentation of normal findings.
Impression / Conclusion Section
- Summarize key findings relevant to the indication
- Use conservative, non-definitive language
- Avoid etiological certainty unsupported by ultrasound
- Include relevant negatives when clinically important
Limitations of the Study
- Inadequate bladder distension
- Bowel gas obscuring pelvic structures
- Patient body habitus limiting acoustic window
- Limited characterization of indeterminate pelvic masses
Documenting limitations ensures transparency and medico-legal safety.
Recommendations & Follow-Up (If Applicable)
- Correlate ultrasound findings with clinical and laboratory data
- Consider follow-up ultrasound for interval assessment when appropriate
- Consider further imaging for indeterminate findings based on clinical context
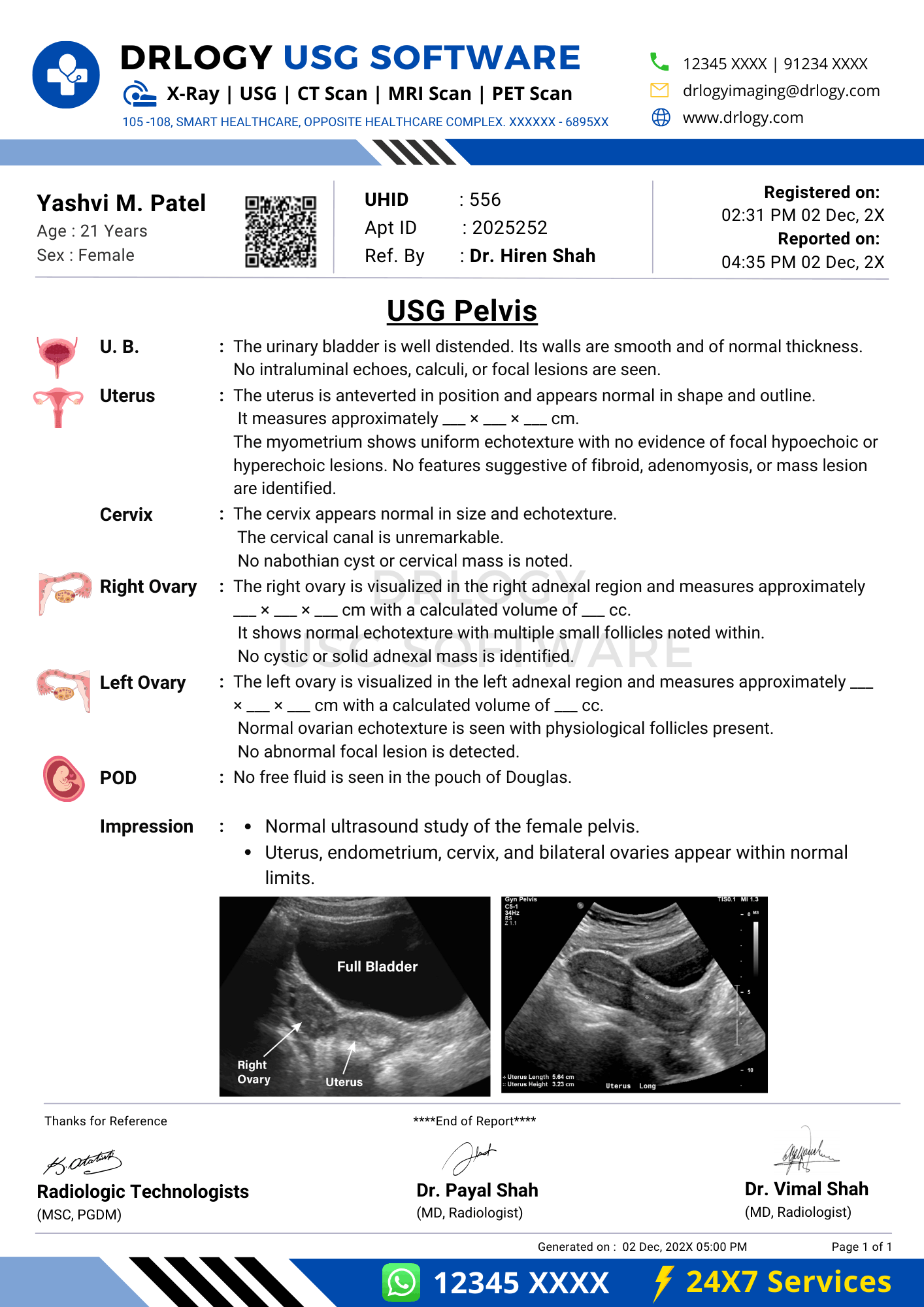
Normal Pelvis Ultrasound Report Format (Sample)
Patient & Study Information:
Patient: [Name], [Age]/[Sex]
Study Date: [DD-MM-YYYY]
Examination: Pelvis Ultrasound
Clinical History / Indication:
Pelvic pain evaluation.
Technique / Protocol:
Transabdominal pelvic ultrasound performed with adequate bladder distension.
Findings:
The uterus is normal in size and echotexture. Endometrial thickness is within normal limits. Both ovaries are normal in size with normal follicular pattern. No adnexal mass is seen. No free fluid isentified in the pelvis. Urinary bladder appears normal.
Impression / Conclusion:
Normal sonographic appearance of the pelvis.
Limitations:
No significant technical limitation noted.
Abnormal Pelvis Ultrasound Report Format (Sample)
Patient & Study Information:
Patient: [Name], [Age]/[Sex]
Study Date: [DD-MM-YYYY]
Examination: Pelvis Ultrasound
Clinical History / Indication:
Abnormal uterine bleeding.
Technique / Protocol:
Transabdominal pelvic ultrasound performed.
Findings:
The uterus appears enlarged with a well-defined hypoechoic intramural lesion measuring [ ] cm, suggestive of a fibroid. Endometrium appears within expected thickness. Ovaries are visualized separately and appear normal. Minimal free fluid is noted in the pelvis.
Impression / Conclusion:
Uterine lesion as described. Clinical correlation is advised.
Limitations:
Assessment limited by bowel gas.
How Drlogy Radiology Reporting Software Standardizes These Report Formats
- Template-driven reporting ensures uniform pelvic organ documentation.
- Impression safety controls promote conservative wording and avoid overstatement.
- Uniform formatting across modalities supports continuity of care.
- AI-enabled reporting assistance supports structured report generation under radiologist supervision.
- Audit-ready documentation improves quality assurance and medico-legal review.
10 Key Clinical Guidelines for an Effective Pelvis Ultrasound Report Format
- Always document examination approach and bladder status.
- Measure and record pelvic organ dimensions consistently.
- Describe lesions objectively before interpretation.
- Use standardized terminology for pelvic pathology.
- Document adnexal structures bilaterally.
- Include Doppler findings only when performed.
- Separate findings from impression clearly.
- Document limitations explicitly.
- Maintain consistent report structure.
- Align impression with clinical indication.
Consistent adherence improves reporting accuracy and medico-legal safety.
Common Reporting Errors to Avoid
- Omission of ovarian or adnexal evaluation
- Inconsistent uterine measurement documentation
- Overinterpretation of indeterminate pelvic lesions
- Failure to document bladder status
- Missing limitation statements
Avoidance of these errors enhances report credibility.
Medico-Legal Considerations in Radiology Reporting
- Objective documentation of findings
- Explicit limitation statements
- Conservative impression language
- Clear accountability and report authorization
- Audit-ready structure
- Appropriate disclaimers
- Accurate comparison statements
Medico-legal robustness depends on completeness and conservative interpretation.
Structured Reporting vs Narrative Reporting
| Aspect | Structured | Narrative |
|---|---|---|
| Completeness | High | Variable |
| Consistency | Standardized | Operator dependent |
| Audit readiness | Strong | Limited |
| Efficiency | Optimized | Variable |
| Medico-legal safety | Enhanced | Variable |
Role of Technology in Radiology Reporting
- PACS and RIS integration
- Voice dictation with templates
- AI-assisted formatting
- RIS-based structured templates
- Modality-specific reporting tools
Technology enhances consistency without replacing professional judgment.
Why High-Volume Radiology Centers Prefer Software-Based Reporting Formats
- Faster turnaround time
- Improved quality assurance
- Multi-radiologist consistency
- Enhanced scalability
- Reduced omission errors
- Audit-ready reporting
- Improved medico-legal protection
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What defines a standard pelvis ultrasound report format?
A structured format documenting pelvic organs, findings, impression, and limitations using conservative terminology.
Should Doppler be included in all pelvic ultrasound reports?
Doppler should be documented only when clinically indicated and performed.
How should indeterminate pelvic masses be reported?
By objective description with conservative language and recommendation for correlation when appropriate.
Why are limitations essential in pelvic ultrasound reporting?
They document reduced sensitivity and protect medico-legal defensibility.
Key Takeaways for Radiology Professionals
- Use a standardized structure for every pelvis ultrasound report.
- Document pelvic organs systematically and bilaterally.
- Maintain conservative impression wording.
- Explicitly state limitations when present.
Consistent structured reporting improves diagnostic clarity and medico-legal safety.
Expert Picks
Final Conclusion
A standardized Pelvis ultrasound report format is essential for accurate clinical communication, reliable follow-up, and medico-legal safety in routine pelvic imaging practice.
Structured reporting software supports consistency, completeness, and conservative interpretation while aligning with real-world radiology workflows and professional standards.